Budgets are tighter than ever. Clients are as innovative as they've ever been. They've seen a competitor do this great new campaign (everyone's talking about it!) and they want something "just like it", because they're sure it's worked like a dream, even though they haven't done a Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA).
This scenario is fairly standard agency practice. Ask anyone who's worked at an agency. In fact, one of the things agency founders struggle with most is to have their clients see campaigns for what they really are, not what they seem to be. According to Proxima, up to 60% of marketing budgets are wasted due to inefficiencies in execution and planning. This is money that could have been put to better use if the failed campaigns had actually gone through a detailed Cost-Benefit Analysis to establish if they were, in fact, worthwhile ventures!
By taking the time to weigh up the costs of a project against what you can expect to get out of it before you even commit, your agency can make the best use of its limited resources and spend time on projects that actually deliver a profit for you and your client.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Visualizations
Visualizing your cost-benefit evaluation can help you understand the data and make the right decisions. You can do that with the help of graphs, cost-benefit analysis matrix, cost-benefit analysis diagrams, cost-benefit curves, and cost-benefit analysis charts:
Graphs: Graphs are a simple yet effective way to illustrate a project's costs and benefits over time. They can clearly show when and how costs are expected to be incurred and when benefits will start accruing.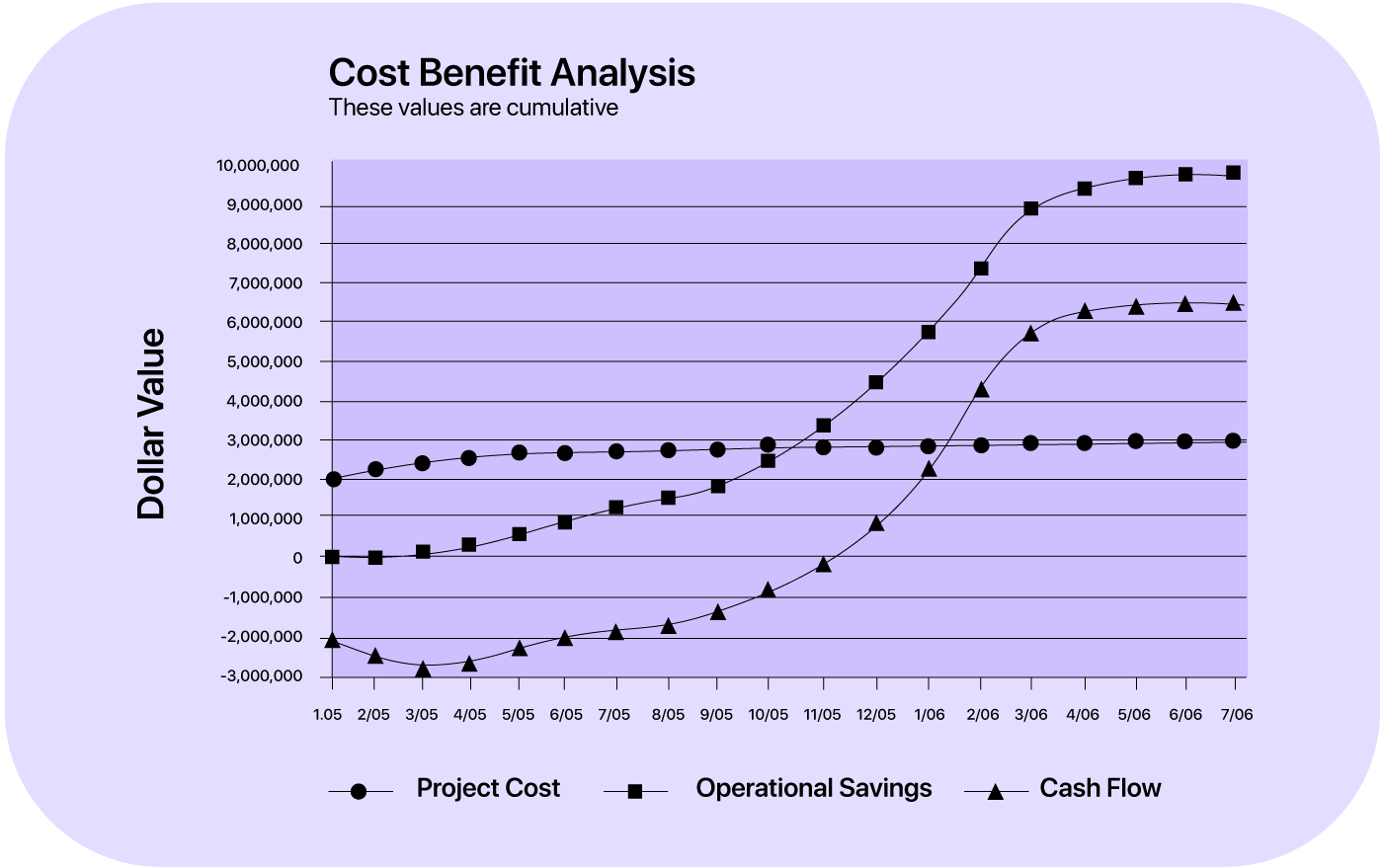
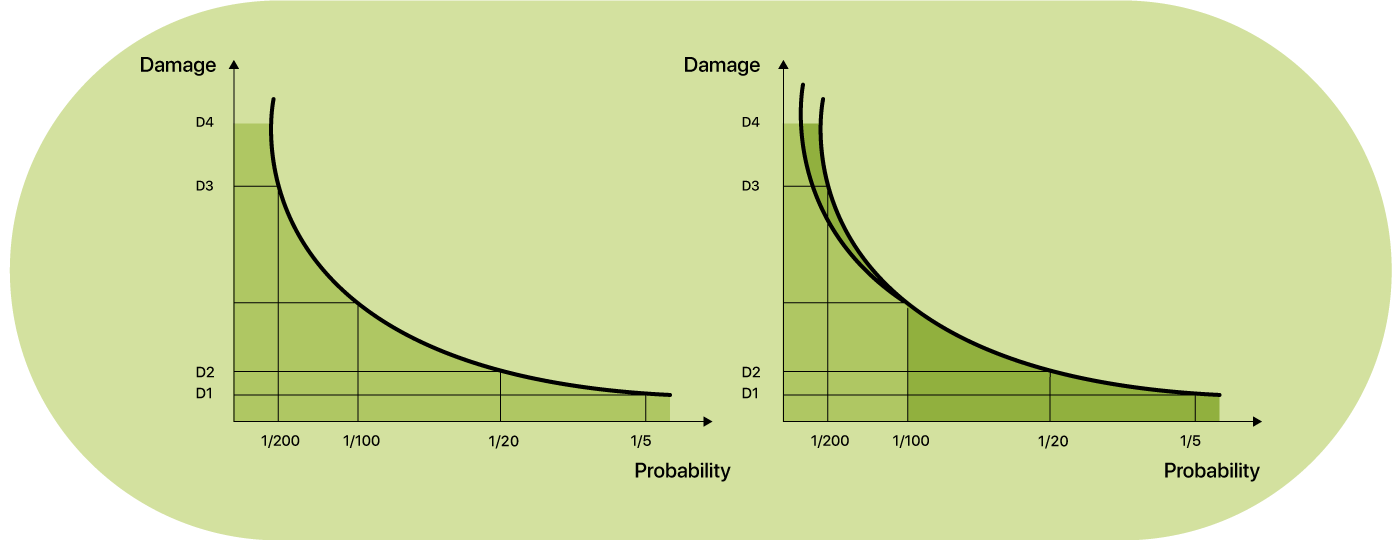
Cost-Benefit Curve: A cost-benefit curve is useful for visualizing the relationship between different levels of investment and the corresponding benefits. The point where the benefit line intersects the cost line represents the optimal level of investment.
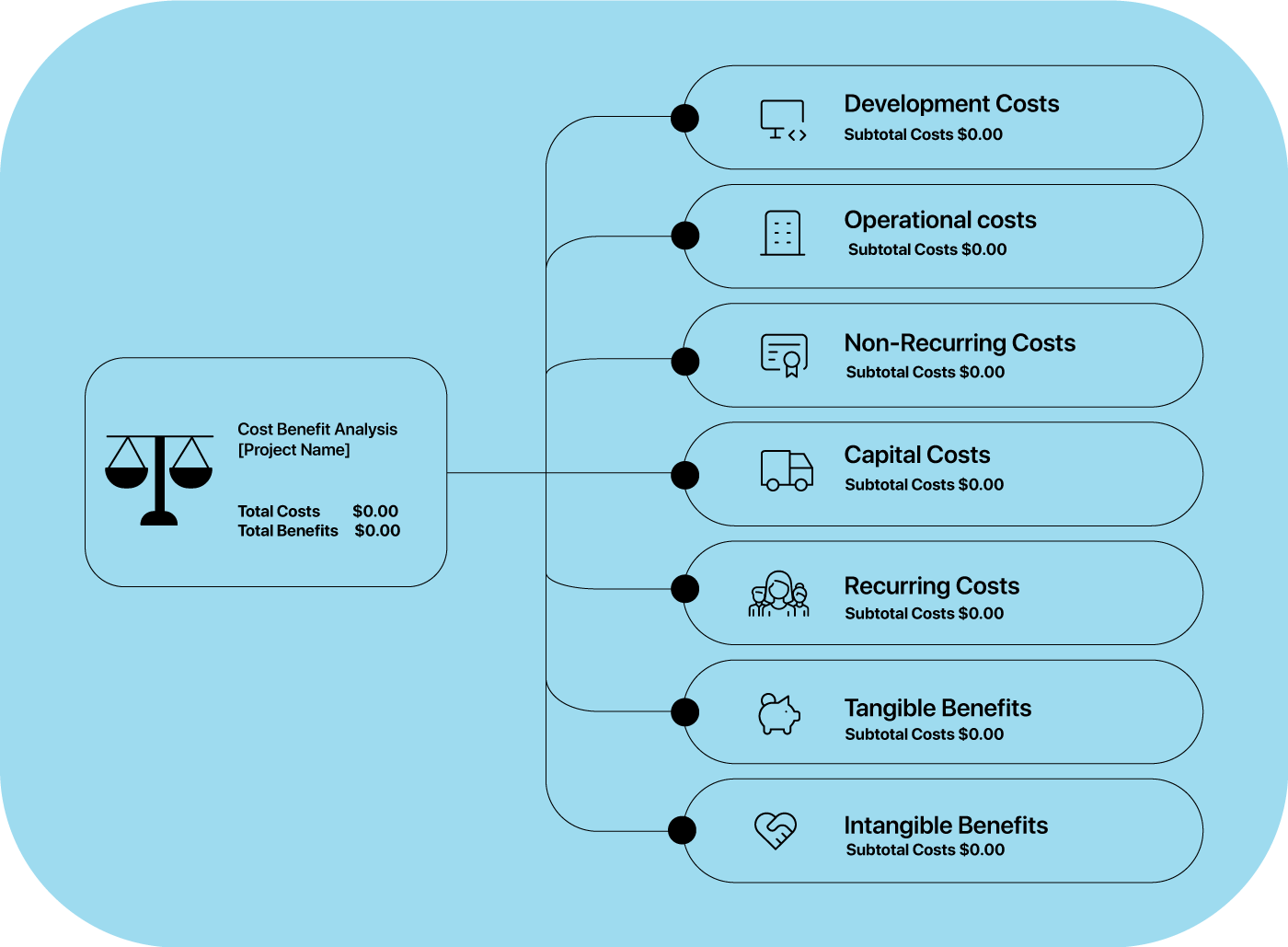
Cost-Benefit Analysis Matrix: This handy tool helps you compare the potential costs and benefits of a project or decision.
6-Steps to conduct a cost-benefit analysis
Doing a cost-benefit analysis sounds messy, and it can be – but if you get the basics right, apply a bit of discipline, and follow a practical approach, it can only take you to a positive (shall we say "profitable") place.
And that's why project managers do them: so they avoid the most common project pitfalls, and don't end up wasting time and money on campaigns that don't deliver a return for them or their clients.
If you want to do a proper cost-benefit analysis for a marketing project, client campaign, or whatever other client initiative, there are six steps you need to follow.
Step 1: Define project or scope and success metrics framework
Every cost-benefit analysis should start with a clear-cut definition of:
What you are analyzing (this is your project scope and timeline)
How will you analyze it ( these are your goals and the success metrics you'll use)
To get those two things right, you'll also need to reach out to and involve key stakeholders who will guide you in the right direction.
Who are they? They are the people and groups that will be affected by the project or campaign. This could include:
- Clients
- Various departments that need to work together to deliver the project
- External consultants or stakeholders
The final thing you'll also need to factor into your scope more specifically your success metrics, are the external factors that could impact your end result. These might be:
- Market conditions
- Current business or industry environment
- Regulatory changes
Looking back at your project plan and mapping out your stakeholders will help you avoid missing anything.
Tip: If you're an agency, you might want to consult your account managers, creative leads, and finance people to understand the project's potential and full impact. Getting everyone on board and brainstorming together early will minimize the chance of missing vital direct costs, indirect costs, or unforeseen future costs that can have a huge impact later down the line when it may be too late!
Step 2: Identify all costs and benefits
The next step is landing a complete list of costs and benefits. Sounds super simple, but it can take some time, and it helps if you don't do it alone, just so you minimize the chance of missing something important.
The best way to do this is to divide your costs into three buckets:
Direct costs: These are the obvious expenses that get tied directly to project execution. They're the easiest to identify and pin down accurately.
Indirect costs: These are your overheads. It includes support services and secondary expenses that are a result of your project.
Opportunity costs: These are a bit more abstract and harder to put a number on. They represent the value of alternative projects or initiatives you'd have to forgo if you commit your resources to this project.
Next, it's time to do the same for all your benefits. When you get to this step, you'll notice that some of your benefits might be hard to quantify. If you have some historical data from past projects or scenarios, it's a goo idea to use those figures as a guide so you're not wildly guessing.
Remember, you'll have two types of benefits:
- Tangible benefits: Most of the time, these are the measurable, positive outcomes that have an actual number. For example, it could be increased revenue, cost savings from process improvements, or efficiencies that lead to overhead cost reductions.
- Intangible benefits: These are almost impossible to put a figure on. They are more conceptual in nature. Intangible benefits are things like an increase in positive media coverage and a spike in brand reputation or competitive positioning.
Tip: Remember, the best and most effective Cost-Benefit Analysis is the most comprehensive one. So make sure you involve all key stakeholders when compiling this list of costs and benefits. The more perspectives and departments you have in your brainstorming team, the more likely you are to cover everything!
Step 3: Assign monetary values to costs and benefits
Step three of the cost and benefit analysis is all about getting the numbers right. This means you need to assign a number to the expected costs and expected benefits that is neither over nor under the realistic value.
One piece of advice we can give you for this bit is to use a combination of:
Hard data (if your project management tool collects historical data like ActiveCollab, you'll have that!)
Industry benchmarks (online research will cover this part)
Careful estimation techniques (this is where experience with similar projects comes in handy!)
In this step, you'll be able to divide all costs and benefits into one of two core categories:
Tangible: These are tangible costs and tangible benefits that have a clear monetary value you can assign immediately. These are things like a freelancer that costs $100 p/h or a software subscription that costs $1200 p/a.
Intangible: These are intangible costs and intangible benefits that need to be analyzed, estimated, and calculated as accurately as possible based on the information you have at your disposal. They can be things like indirect cost benefits, like money earned because your team saved 10 hours on a task by using an automation tool.
Tip: When you don't have clear numbers, be very careful and conservative with estimates. Use ranges instead of point estimates for any uncertainties (instead of saying $50,000 in annual savings, say $40,000 to $60,000). At all costs, avoid the temptation to underestimate costs and overestimate benefits. This is a common problem for new projects during cost-effectiveness analysis.
Step 4: Calculate the Present Value (PV) and Net Present Value (NPV)
Step four asks you to get down and dirty with some financial mathematics. It's all about getting your head around the time value of money, which isn't always immediately apparent.
Basically, a dollar in your hand right now is worth a heck of a lot more than a dollar you'll get in a few years. The reality of many projects is that they'll incur costs upfront and only become profitable later, or vice versa.
So if you're going to make a fair comparison, you need to use a discount rate. This is the rate used to convert future costs and benefits into today's value.
The Present Value formula is:
PV = FV ÷ (1 + r)^n
Where:
FV represents future value
r equals your discount rate
n indicates the time period
Scenario example:
Let's say you're a marketing agency with 30 people and you're weighing up whether to take on a global client that's going to need a whole lot of investment over a 12-month contract.
The breakdown of costs and benefits is listed in the table.
| Costs | Benefits | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Creative asset production | $60,000 (upfront) | Monthly retainer | $35,000 ($420,000 annual) |
Market research | $25,000 (upfront) | Assume a 10% chance of the client cancelling halfway | $378,000 |
New hires | $10,000 p/m ($120,000 annual) |
Total upfront (year 0): $85,000
Ongoing annual costs: $135,000
To get the PV, you need to:
Work out the present value for each year's costs & benefits separately
Add them all up to get the total present value for that category
Taking this year-by-year approach helps you see when the actual costs and benefits are going to fall due, which is really important if you're planning your cash flow and trying to work out the risks you'll be taking on.
The PV for the above scenario would look like this:
Year 0: -$85,000 ÷ (1.10^0)= -$85,000
Year 1: $243,000 ÷ (1.10^1) = $220,909
To calculate Net Present Value, use the formula:
NPV = ∑ [(Benefit - Cost) ÷ (1+r)^n]
In simple terms, this is the sum of all present value benefits minus the sum of all present value costs.
If we apply the example from above, the NPV calculation will look like this:
NPV = -$85,000 + $220,909
= $135,909
A positive NPV means benefits exceed costs when properly adjusted for timing, suggesting the project is a worthwhile investment for your organization.
Tip: Choose a realistic rate and apply it consistently. The most common rates range between 5-10% (depending on industry and business context). Also, remember that your NVP will only be as good as the forecasts and rate you've used to calculate it.
Step 5: Calculate and track your Benefit-Cost Ratio
Another useful metric to have as part of your overall cost-benefit analysis is the Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR). This number tells you how your total Present Value (PV) benefits compare to your total present value costs.What it essentially tells you is the return for each dollar spent.
The Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR) formula is:
BCR = Total Present Value of Benefits ÷ Total Present Value of Costs
If we use the example from above, our BCR would look like this:
PV of benefits = $378,000 ÷ 1.10 = $343,636
PV of costs where:
Year 0: $85,000÷1 = $85,000
Year 1: $135,000÷1.10 = $122,727
PV of costs = $85,000 = $122,727 = $207,727
Now we can calculate our BCR:
BCR = $343,636 ÷ $207,727 = 1.65
A BCR of 1.0 or more: Says that the benefits exceed the costs of an investment. Meaning, the project is worth the money.
However, lots of organisations have a minimum acceptable BCR threshold of between 1.2 and 1.5 to account for uncertainties that come with estimates, hidden costs, and unaccounted overhead expenses.
Tip: The benefit-cost ratio is a great comparative tool, but don't rely on it alone for key business decisions. It should be used strictly as a complementary guide (alongside other metrics and the realistic business environment), to understand the projected revenue and potential dollar value of the proposed project.
Step 6: Perform sensitivity analysis and make a decision
Now that you have your core metrics (NPV and BCR), you've got a good indication of whether your project's benefits outweigh its costs. The next step is to add some robustness to your findings by adding sensitivity analysis.
In simple terms, sensitivity analysis involves tweaking key assumptions and seeing how the results change.
This is your typical:
"What if instead of this, this other thing actually happens? What will my results look like then?
For sensitivity testing, you can trial changing
- Labor costs by ±20%
- Modify revenue projections by ±15%
- Adjust your discount rate by ±2%
By adjusting these variables and recalculating NPV or BCR, you can spot which assumptions the analysis is most sensitive to. But why is this important? Because it highlights your greatest project risk factors.
So if your project only looks good under very specific assumptions, you should take that as a warning sign.
For example, that warning might come in the form of a discovery that a slight change makes your NPV turn negative, or it makes your BCR dip below 1.0.
On the other hand, if your project remains solid and still beneficial even under pessimistic scenarios (say, if benefits that are 20% lower still produce a positive NVP), you can be confident the project is very much worth the investment.
Tip: When you do sensitivity testing, create at least three scenarios: base case (your most likely assumption), best case (your most optimistic scenario), and worst case (your most pessimistic scenario).
Using cost-benefit analysis in projects and agency management
Cost-benefit analysis is a practical and useful tool that agency and project managers use to better understand the profitability and viability of their client campaigns and projects.
If you run a marketing or consulting agency, you can use the CBA in several ways:
Project selection and prioritisation
Agencies often juggle a bunch of different project opportunities, from new client campaigns to internal initiatives and expanding current client portfolios. A CBA gives you a way to work out which projects are going to pass with flying colours, and which ones are going to die a slow (and costly!) death.
By comparing the costs and. benefits, you'll know which projects to go with and which to walk away from quickly.
Budgeting and resource allocation
With tight budgets and limited headcounts, agencies have to be really strategic about where, when. and how to invest resources and do their capacity planning. Doing a cost-benefit analysis is a great way to get more bang for your buck, by evaluating the potential benefits and working out if a proposed project is worth the budget it's going to take to deliver.
Knowing which project or campaign is going to give you the best return on investment also helps you make smarter decisions about how you spend the time and money you have.
Risk management and planning
Every project comes with risks, whether they be scope creep, delays, or cost blowouts. A proper CBA gets you to think about all the things that could go wrong, before they actually do, so you can understand the dollar value of those mistakes.
This means you can proactively plan to mitigate those risks based on a rational assessment of the costs versus the benefits.
Stakeholder communication and buy-in
When you present a project proposal to clients, executives, or team members, backing it up with a cost-benefit analysis lends a level of credibility that's hard to knock back. Because you have the data on hand, getting buy-in is much easier.
It also gives you a level of transparency that builds trust and confidence.
What Can a Cost-Benefit Analysis Really Do for You?
A solid cost-benefit analysis can be a work-changing tool that can do a world of good for decision-makers in agencies and consulting businesses.
Here are four of the main benefits of using the Cost-Benefit Analysis approach whenever you need to gauge the viability of a new campaign or client project.
Making decisions based on facts
Cost-Benefit Analysis gives a clear, no-nonsense approach to making decisions. You ditch the gut feeling and instead start evaluating choices based on hard numbers. This means you're less likely to let bias and emotions take over.
Getting a clear reason behind your decisions
By breaking down costs and benefits, Cost-Benefit Analysis gives you a clear reason why a project should or shouldn't go ahead. And that lets you compile a simple and clear business case that you can present to stakeholders.
It's handy for getting buy-in, but it also creates accountability. If you do decide to go ahead, you can then check in down the line and ask, "Did that campaign deliver the $100k net benefit we thought it would?" Having that benchmark is a great way of encouraging learning and taking responsibility for the results.
Really thinking through a project
Doing a Cost-Benefit Analysis forces you to look at all the angles, and not just the usual suspects. You get to uncover direct costs, intangible costs, future costs, and spot potential risks before you invest a cent into the project.
By doing a thorough cost-benefit analysis, in the end, you're going to get a much fuller picture of the project's impact. You're going to surface any hidden associated costs and issues and reevaluate estimated costs, so you can work out if the total expected costs will be worth the time and money.
Making your strategic planning smarter
The more time you do a Cost-Benefit Analysis, the more knowledge you gather about what works and what doesn't for your business. You start to spot patterns (like certain types of projects that always end up as failures!). And that data-driven insight makes your strategic planning way more effective.
Over time, you can refine what you do and focus on the projects with the best cost-benefit profiles.
In a nutshell: A Cost-Benefit Analysis acts as a safety net and a guide. It keeps you from doing something just because you've always done it, or because a client is keen, and points you in the direction of initiatives that have actual value. And in a competitive space like marketing and consulting, that can mean you perform better for your clients and come out on top financially!
Limitations of cost-benefit analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is a great tool for making decisions, but you cant just put your faith in it. Understanding its limitations will keep you from relying on it too much.
Sometimes, it's hard to land the right price
The truth is, not everything that counts can be put into numbers. Benefits like "boosting the image of your brand" and costs like "burning out your employees" are super tough to put a price on. When you do try to put a value on them, the numbers are usually just a guess and they're often way off. Misjudging these values can make your project look better or worse than it actually is. Handle these kinds of values with care and do some sensitivity analysis to test your assumptions.
Forecasting is not always accurate
Cost-benefit analysis relies on making a bunch of projections about things like how much money you'll make, how much it will cost you, how fast you'll grow, and how fast inflation will rise. Even a small mistake can totally mess up the results. The market can shift, your competition can change, or the economy might surprise you with a big change. So when you do cost-benefit analysis, be aware it's not a perfect science.
CBAs can be a drain on your resources
Doing a detailed analysis takes a lot of time, a lot of data, and some serious expertise. For smaller projects, it's often the case that the cost of doing the analysis is just too high to be worth it. Instead, just use CBAs when it's a large-scale, high-cost project, and rely on simpler tools or your personal judgment for the smaller stuff.
Your own biases can affect the results
The people doing the analysis can accidentally shape the outcome of the numbers by the way they pick the data or put a value on things. And if someone has a personal stake in how the project turns out (either good or bad), they can skew the results.
ActiveCollab: The tool that stores all your project costs data
Doing a cost-benefit analysis as an agency can be a real challenge. First of all, just getting a hold of accurate data is a major pain point. But tools like ActiveCollab can make it much easier than you think.
Because ActiveCollab lets you set up projects with budgets and lets you manage costs and expenses as the project progresses, all the cost data is collected in real time. The platform essentially gathers historical project cost data, which you can then view, analyse, and use to understand a project's profitability.
When a project finally wraps up, you can generate dashboards and reports that give you a super clear picture of where all the time was spent, who worked on what, and exactly how the budget breakdown looked. And from there, you can take all that information and use it to make way more informed guesses about costs and benefits so you can plan future projects with certainty.
Ultimately, what ActiveCollab is really all about is keeping agencies profitable by sorting out their project data for them.
When you have the data, to do a proper Cost-Benefit Analysis, you can plan client campaigns and projects, manage resources, do some capacity planning, and actually run the whole show from start to finish without worrying about the end result.
Rather than jumping all over different apps in an attempt to get a handle on your project finances, ActiveCollab lets you keep everything in one place - right from that initial client estimate all the way through to the final invoice and all that post-project profit reporting.
Need a tool that centralizes project, client, and financial management? Check out ActiveCollab.
Sign up for our 14-day free trial or book a demo with one of our people to see how the tool works.