Theory of Constraints
The Theory of Constraints lets companies optimize their processes and maximize their results. We’ll discuss the central concept and principles behind the theory, explore its importance, and show through examples how it works in practice.

What is the Theory of Constraints?
The Theory of Constraints is a methodology that helps you identify the crucial limiting factor (usually referred to as a constraint or a bottleneck) that stands in the way of achieving a goal. The main goal of the Theory of Constraints is to improve that constraint to the point when it’s no longer the limiting factor.
In his bestselling novel “The Goal” (1984), Dr. Eliyahu Goldratt developed the Theory of Constraints (TOC) and introduced it to a wide audience. Since then, TOC has continued to evolve, and today it is one of the most well-known management techniques.
The Theory of Constraints has had a tremendous impact on the business world and has produced remarkable results for companies worldwide.
Despite the popular belief that Goldratt’s Theory of Constraints applies only to the manufacturing environment, it has had a major effect on other industries as well (including IT). It has also been developed for various industries, such as retail, banking, logistics, healthcare, etc.
The Goal of the Theory of Constraints
The Theory of Constraints hypotheses that every complex system, including manufacturing processes, consists of multiple linked activities, where one of them can disrupt the whole system (i.e., “weakest link in the chain”).
The goal of the Theory of Constraints is to make a profit. Tools that will help you achieve that goal are:
- The Five Focusing Steps - a methodology that helps you identify and eliminate constraints.
- The Thinking Processes - tools that help you analyze and resolve problems.
- Throughput Accounting - a method that helps you measure performance and guide management decisions.
What are the Constraints in Project Management?
In the Theory of Constraints, a constraint is the obstacle that prevents you from achieving your goal. There are six types of constraints that can prevent the team from achieving the project goals:
- Scope - the scope of the project can pose a constraint in project management, as scope defines specific goals, deliverables, and features that should be completed.
- Quality - the quality constraint focuses on the quality of the project that is set early in the planning stages.
- Risk - the risk constraints include both internal and external factors that could jeopardize the project’s outcome.
- Resources - the availability of necessary resources to complete the project.
- Budget - the amount of money needed to complete the project on time.
- Schedule - time or schedule is the amount of time which is needed to complete the project on time with available resources and meeting the set budget.
Bottleneck Theory of Constraints
Although used as synonyms, bottlenecks and constraints aren’t the same thing. Constraints can be bottlenecks, but not every bottleneck is a constraint. A bottleneck can be a temporary roadblock that creates delays and piles up work-in-progress. Constraints have a much more significant impact because they affect the whole system. This is why all other operations must be subordinated to them in order to optimize the flow.
Bottlenecks reduce the capacity of a resource and must be identified to be eliminated. Sometimes, bottlenecks can be an external factor, such as red tape, but they can hinder the organization’s productivity nonetheless. If the bottleneck persists, radical steps need to be taken so a workaround or an adequate solution can be found.
Examples of Constraints
Examples of constraints and bottlenecks can be found in any industry and type of organization. Hospitals can be faced with long waiting times, software teams with inefficient team members, and a digital marketing agency with client feedback delays. The principles of TOC dictate that the constraint must be identified. Managers should use visual tools to break down the workflow and find what’s causing the system to not work properly.
Next, the identified resource should be improved by making simple changes. In our examples, this could include making a scheduling system for patients, letting the burnt-out colleague get some days off so they can perform better, and communicating with clients on a daily basis.
All other parts of the system should support the identified constraint. Doctors shouldn’t make appointments that clog the schedule, no additional assignments should be given to the burnt-out employee, and no extra design changes should be made without the client’s explicit request.
If these remedies aren’t sufficient, you should consider investing in better solutions, such as project management tools that will map out all the processes and facilitate communication and collaboration. Once the constraints are resolved, managers and teams should be on the lookout for new ones so the workflow can be continuously improved. Constant improvement is a principle shared with other methodologies like Six Sigma and Lean.
Theory of Constraints Five Focusing Steps
The five focusing steps are the cyclical process aimed at improving and eliminating bottlenecks you encounter on almost any project. They include the following steps:
Identify
The first step in solving any problem is identifying it. So, the Theory of Constraints says that the current constraint should be found in the chain of activities. It’s a factor that hinders the organization from achieving the best results. Once you learn how to identify bottlenecks, it will become easier and quicker to find them.
Exploit
Make quick improvements by using existing resources. Before making any new investments, you should try to squeeze out as much output as possible from the constraint. It’s important to eliminate any obstacles that cause the resource to underperform.
Subordinate
Review all the activities to ensure they support the needs of the constraint. All the other activities should be managed in a way that doesn’t produce waste. The production should be adequate so it meets the constraint's capacity and doesn’t create excess work-in-progress.
Elevate
Take action until the restraint has been eliminated. In some cases, this may require major investments. If the constraint isn’t eliminated after being exploited and all the available resources have been used and subordinated to it, it’s time to elevate the constraint’s capacity by elevating the technology with additional investments.
Repeat
After resolving one constraint, repeat the cycle and work on improving new constraints that pop up. Making changes around one constraint could create new constraints elsewhere because of the new working conditions. This process is continuous and requires constant revision.
The Thinking Processes
The Thinking Processes are mainly used for complex systems with many activities that depend on one another. They are designed as scientific “cause and effect” tools. Their role is to identify the root causes of undesirable effects (referred to as UDEs) and then remove the UDEs without developing new ones.
The Thinking Processes help you answer three vital questions:
- What do you need to change?
- What should you change it to?
- What actions will cause the change?
The classic thinking process tools include:
- Current reality tree (CRT)— Visual representation of cause-and-effect relationships where the “Un-Desirable Effects” (UDEs) trace back to their root cause.
- Evaporating Cloud (EC)— Identifies hidden assumptions so the core conflict can be resolved and any dilemmas eliminated.
- Future Reality Tree (FRT)— Visually represents the changes that can solve the issues identified in the CRT. The FRT maps how UDEs can be eliminated.
- Negative Branch Reservation (NBR)— Shows the challenges that could arise when implementing a solution, and by anticipating problems helps mitigate them.
- Prerequisite Tree (PRT)— Identifies all the requirements that need to be met so a solution can be implemented successfully.
- Transition Tree (TT)— Offers a detailed set of activities needed to implement a solution and reach the desired goal.
- 3-Cloud Method— Combined with TOC principles and Strategy and Tactic Trees, it provides a step-by-step guide to achieving a successful implementation of a solution.
Throughput Accounting
Unlike traditional accounting (where there is a strong emphasis on cutting expenses, which are limited by reaching zero expenses), the Theory of Constraints focuses more on increasing the profit, so it doesn't have such limitations.
According to the Theory of Constraints, inventory ties up cash you can use more productively elsewhere. Overall, the Theory of Constraints attempts to eliminate distortions that promote goals contrary to increasing profit.
Throughput accounting has four measures:
- Net profit
- Return on investment
- Productivity
- Investment Turns
Essentially, there are three improvements you should be focusing on:
- Will throughput be increased?
- Will investment be reduced?
- Will Operating Expenses be reduced?
What is Drum-Buffer-Rope in the Theory of Constraints?
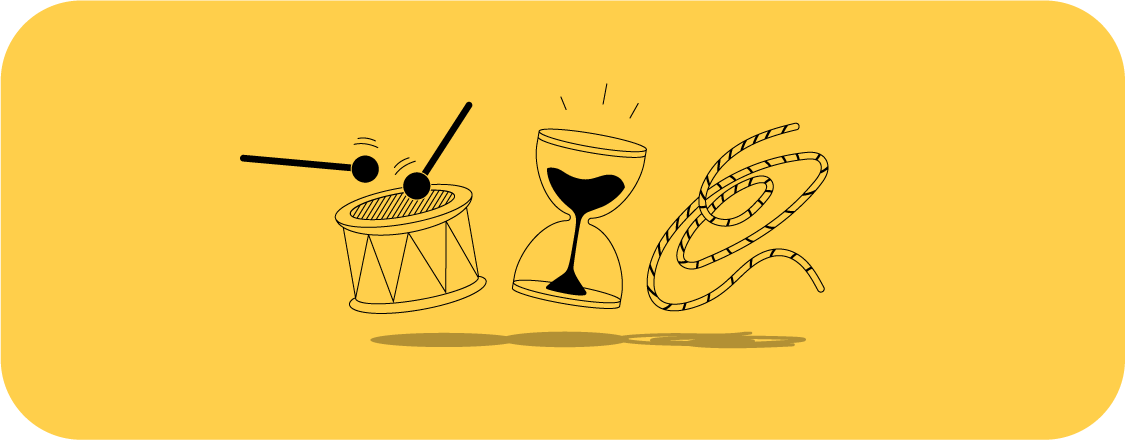

Just like the Theory of Constraints, the drum-buffer-rope (DBR) method was developed by Dr Goldratt. In this method, the drum is the constraint because it dictates the rhythm of the entire production process. If the constraint isn’t optimized, all the other resources will have to pace their outputs accordingly.
The buffer is time. More precisely, it is the amount of work prior to the constraint measured in time. It ensures all variability, uncertainties, and unforeseen events are absorbed so the constraint doesn’t run out of work. The buffers are divided into the green, yellow, and red zones, where the red shouldn’t be tapped into more than 5% of the time.
The rope controls the work in progress. It signals whether the constraint is ready for new work to be released. The availability of the buffer pulls the rope that tells other resources to prepare more work for the constraint.
Theory of Constraints and Lean Manufacturing/Methodology
The Theory of constraints complements the lean methodology. Both Lean and TOC aim to increase profit. Lean, however, aims to increase profit by making the product more valuable to the customer. Lean aims to add value by eliminating waste. The Theory of Constraints, on the other hand, aims to identify the constraints and increase profit by increasing the throughput. As for the results, both of the methodologies can actually give almost instantaneous results, however for the effectiveness of these methodologies to last, they need to be consistently used for a number of years.
How Does CCPM Relate to the Theory of Constraints (TOC)?
The Theory of Constraints is often criticized for being too focused on the manufacturing process. Its principles can, however, be applied to other industries as well, and this is where critical chain project management theory (CCPM) enters the stage.
CCPM is the application of TOC to project management, and it’s guided by the principles of the Theory of Constraints. For starters, the first step of finding the constraint is also used in CCPM, only in a different form. The constraints in a project could be limited resources, task dependencies, or specific deadlines that don’t coincide with the task's estimated duration.
The critical chain is the longest path of dependent tasks necessary to complete a project. It takes into account the availability of resources as a constraint and the uncertainties that follow each assignment’s duration. This way, the entire process is optimized so the project is executed efficiently and delivered on time.
Principles of Flow
The Theory of Constraints can be applied to the whole organization. The principles of flow are the following:
- Optimizing flow— The flow is optimized when all the obstacles are removed, and the processes run smoothly. This principle encourages managers to identify bottlenecks, eliminate unnecessary delays, and make the most of available resources so the workflow is uninterrupted.
- Non-production— The Theory of Constraints emphasizes the production of just the right amount of outputs that meet the capacity of constraints and market demand. It’s important not to create too much inventory that will generate only additional costs.
- Abolishing local optima— The goal of the Theory of Constraints is to optimize the entire process rather than only certain parts of it. The focus is on the weakest links so they can be improved for the benefit of the entire flow.
- Focusing process— Identifying constraints and redirecting all efforts toward them is the focus of the Theory of Constraints. This continuous process allows companies to maximize their output and optimize their processes.
The Benefits of the Theory of Constraints
One of the most beneficial characteristics of the Theory of Constraints is that it emphasizes the process of improvement. In environments with an urgent need to improve, TOC offers the best solution as it focuses primarily on creating rapid improvements.
A successful implementation of the Theory of Constraints has several advantages:
- Improving capacity: By optimizing the constraint, TOC helps companies increase their throughput. The system can generate output at a faster rate, and enabling more products to be manufactured can lead to higher revenue and better financial results, reducing operational expenses.
- Reducing lead time: Once the constraint is identified and solved, the optimized workflow will allow the company to deliver the desired product to its customers more quickly and improve the project process. This will also lead to process improvement, increased customer satisfaction, and increased profit.
- Holistic approach: At first, it may seem that TOC only focuses on certain parts of the process. However, locating and eliminating constraints means creating a smoother and faster product flow in the entire system. The weakest links are improved in the work process so all resources can match the optimal level of production.
- Waste reduction: Once a bottleneck or constraint is identified, the other operations are tuned according to their capacity. This way, excess inventory and work-in-progress are eliminated, and waste is reduced. Although they have their differences, TOC project management philosophy is very similar to the Lean methodology in the aim of reducing waste and improving throughput rate.
Handle Constraints with ActiveCollab
ActiveCollab is a project management software that can help project managers and teams to better handle project constraints, by allowing them to oversee every step of the project’s process and anticipate potential problems and issues lurking. Managing risks that could jeopardize the project’s success is one of the most important aspects of managing a project. ActiveCollab provides the solution to keep the team and the project on the right track to success, and a platform that allows you to handle various aspects of the project successfully.
Continue reading
Project Management Methodologies Introduction
Get familiar with the most popular methodologies modern project managers use! Learn the basics and choose the best method to manage your teams and projects.